Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection that affects the nails. It can cause discoloration, thickening, and brittleness of the toenails, leading to discomfort and aesthetic concerns. Recognizing the symptoms of toenail fungus and seeking appropriate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the common symptoms of toenail fungus and discuss how to diagnose this condition.
Symptoms of Toenail Fungus:
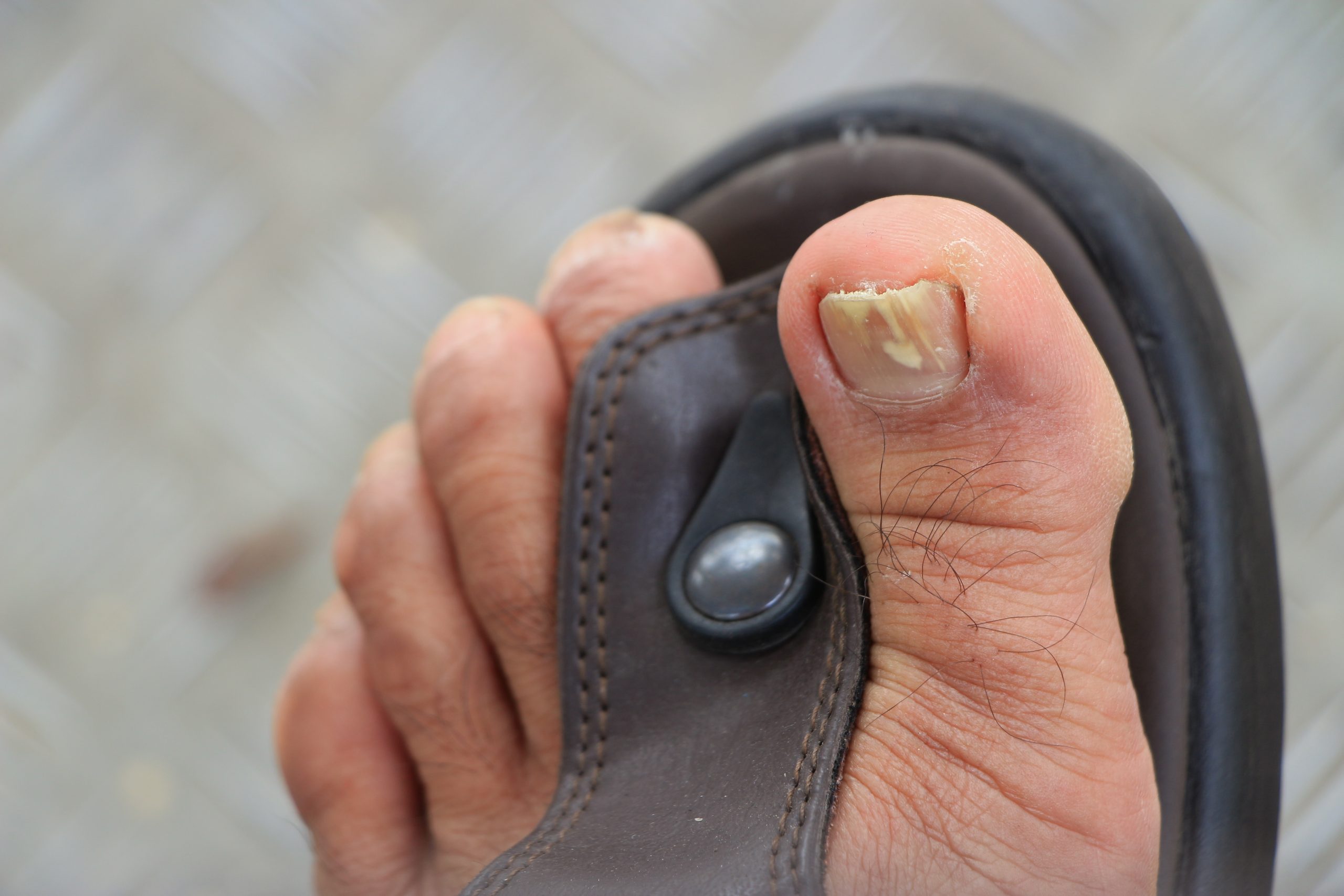
- Discoloration: One of the most noticeable signs of toenail fungus is discoloration of the affected nails. The nails may appear yellow, brown, or white, and the color change can be uniform or in patches. As the infection progresses, the nails may darken or become opaque.
- Thickened Nails: Toenail fungus can cause thickening of the nails, making them appear bulky and distorted. The affected nails may become difficult to trim or maintain, and they may feel uncomfortable or painful in footwear.
- Brittle and Crumbly Texture: Infected nails often become brittle and crumbly. They may easily break or split, and the texture of the nail plate may become rough or uneven. The nails may also separate from the nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis.
- Change in Nail Shape: Toenail fungus can cause a change in the shape of the affected nails. They may become irregularly shaped, curved, or distorted. In some cases, the infection may cause the nails to lift or detach from the nail bed.
- Foul Odor: Fungal infections can produce a distinct and unpleasant odor. Infected toenails may emit a foul smell, especially when moisture or sweat accumulates in the area. This odor can be particularly noticeable when removing shoes or socks.
- Nail Debris: As toenail fungus progresses, it can lead to the accumulation of debris under the nails. The debris may consist of powdery or crumbly material, as well as fragments of the infected nail. This debris can contribute to further nail discoloration and hinder proper nail hygiene.
Diagnosing Toenail Fungus:
If you suspect you have toenail fungus based on the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to seek professional diagnosis for confirmation and appropriate treatment. Here’s how toenail fungus is typically diagnosed:
- Visual Examination: A healthcare professional, usually a dermatologist or podiatrist, will perform a visual examination of the affected nails. They will assess the nail’s appearance, color, texture, thickness, and any associated symptoms. This initial assessment can provide valuable clues for diagnosis.
- Nail Sampling: In some cases, a nail sample may be collected for laboratory testing. This involves trimming a small piece of the affected nail or scraping the nail surface to obtain a sample. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination or culture to identify the specific fungus causing the infection.
- Medical History and Symptoms: The healthcare professional will inquire about your medical history and any symptoms you have been experiencing. They may ask about factors that increase the risk of toenail fungus, such as previous fungal infections, exposure to moist environments (e.g., swimming pools, locker rooms), or certain medical conditions (e.g., diabetes).
- Differential Diagnosis: Other nail conditions, such as psoriasis, eczema, or trauma, can mimic the symptoms of toenail fungus. The healthcare professional will consider these possibilities and perform a differential diagnosis to rule out other potential causes of nail abnormalities.
Once the diagnosis of toenail fungus is confirmed, appropriate treatment options can be discussed. Treatment