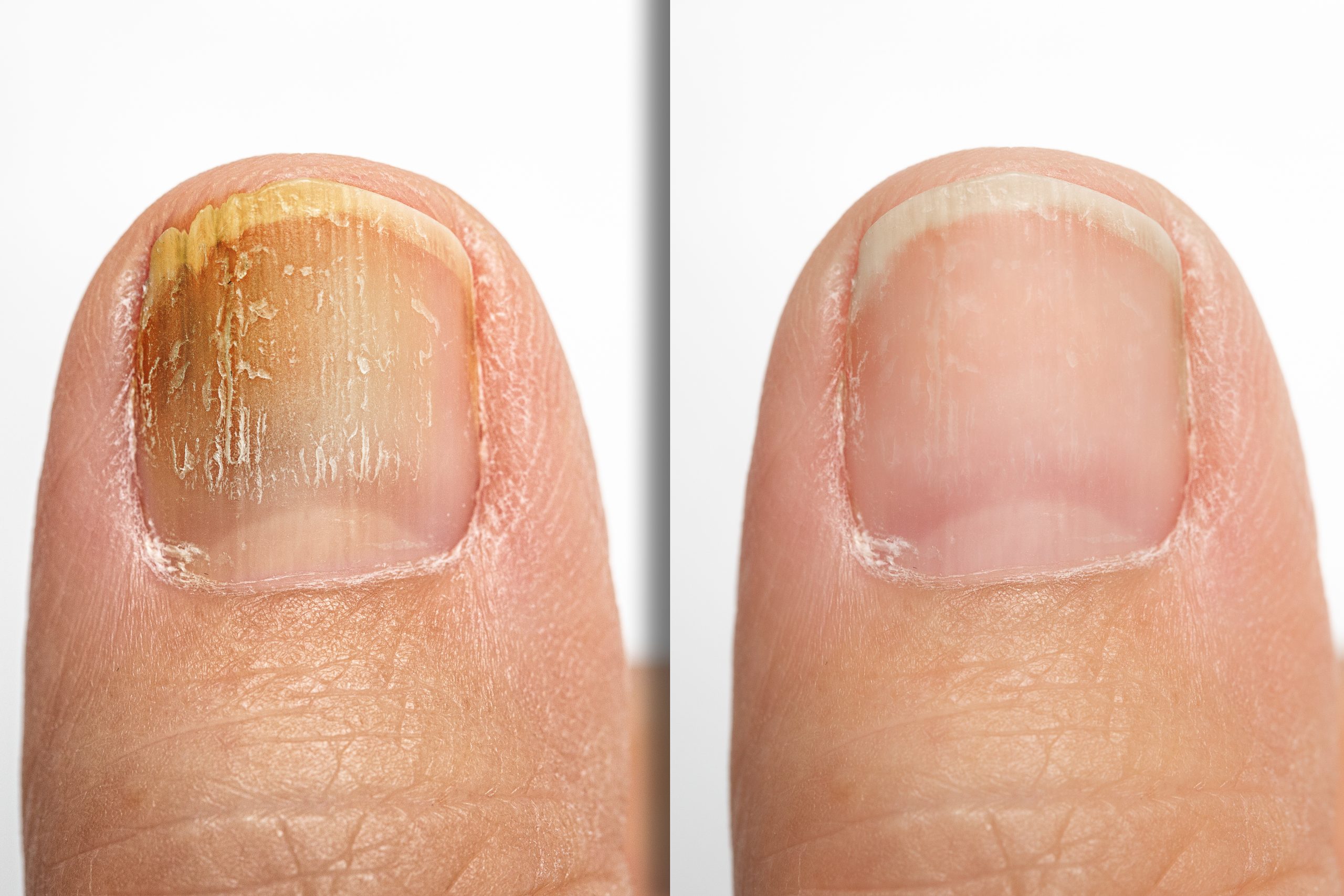
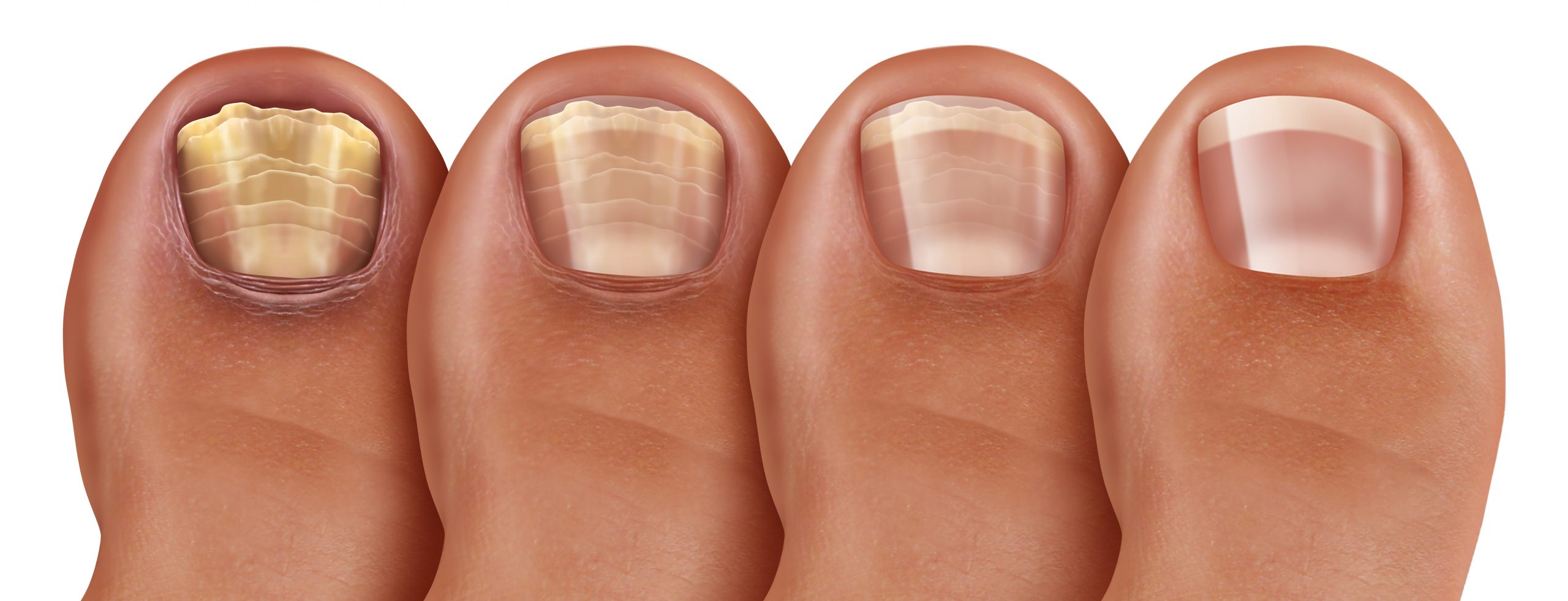
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects many individuals. It occurs when fungi invade the nails, causing them to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. While there are several treatment options available, antifungal medication plays a vital role in effectively treating toenail fungus. In this article, we’ll explore the role of antifungal medication in treating toenail fungus.
Understanding Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus is typically caused by dermatophyte fungi, which thrive in warm, moist environments like shoes and socks. Factors such as poor foot hygiene, excessive moisture, a weakened immune system, and previous nail injuries can increase the risk of developing toenail fungus. If left untreated, toenail fungus can spread and lead to discomfort, pain, and potential complications.
Antifungal Medication for Toenail Fungus
Antifungal medication is a key treatment option for toenail fungus. These medications work by either stopping the growth of the fungus or killing it. There are two primary types of antifungal medication used to treat toenail fungus: topical and oral.
- Topical Antifungal Medication
Topical antifungal medications are applied directly to the affected nails and surrounding skin. These medications are available in the form of creams, gels, or nail lacquers. Topical antifungal treatments are generally recommended for mild to moderate cases of toenail fungus.
When using topical antifungal medication, it’s important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional. The medication is typically applied daily for several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the infection. Consistency and adherence to the treatment regimen are crucial for optimal results.
- Oral Antifungal Medication
Oral antifungal medication is prescribed for more severe or resistant cases of toenail fungus. These medications are taken by mouth and are effective in treating the infection from within the body. Oral antifungal medications may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications, so it’s essential to discuss these factors with your healthcare professional before starting treatment.
Oral antifungal medications are typically taken for a designated period, often ranging from a few weeks to several months. The treatment duration depends on factors such as the extent of the infection, the type of antifungal medication prescribed, and the individual’s response to treatment.
Combination Therapy
In some cases, a combination of topical and oral antifungal medications may be recommended for toenail fungus treatment. This approach can enhance effectiveness, especially for severe or stubborn infections.
Important Considerations
While antifungal medication is an effective treatment option, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Patience and Persistence: Treating toenail fungus requires patience and persistence. Improvement may take time, and it’s essential to follow the treatment plan consistently to achieve the best outcomes.
- Good Foot Hygiene: Practicing good foot hygiene is vital during toenail fungus treatment. This includes keeping your feet clean and dry, regularly changing socks and shoes, and avoiding walking barefoot in public areas to prevent reinfection.
- Consultation with Healthcare Professional: It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They can guide you on the most suitable antifungal medication, monitor your progress, and address any concerns or complications that may arise during treatment.
In conclusion, antifungal medication plays a crucial role in treating toenail fungus. Topical and oral antifungal medications are effective in eliminating the fungus and restoring the