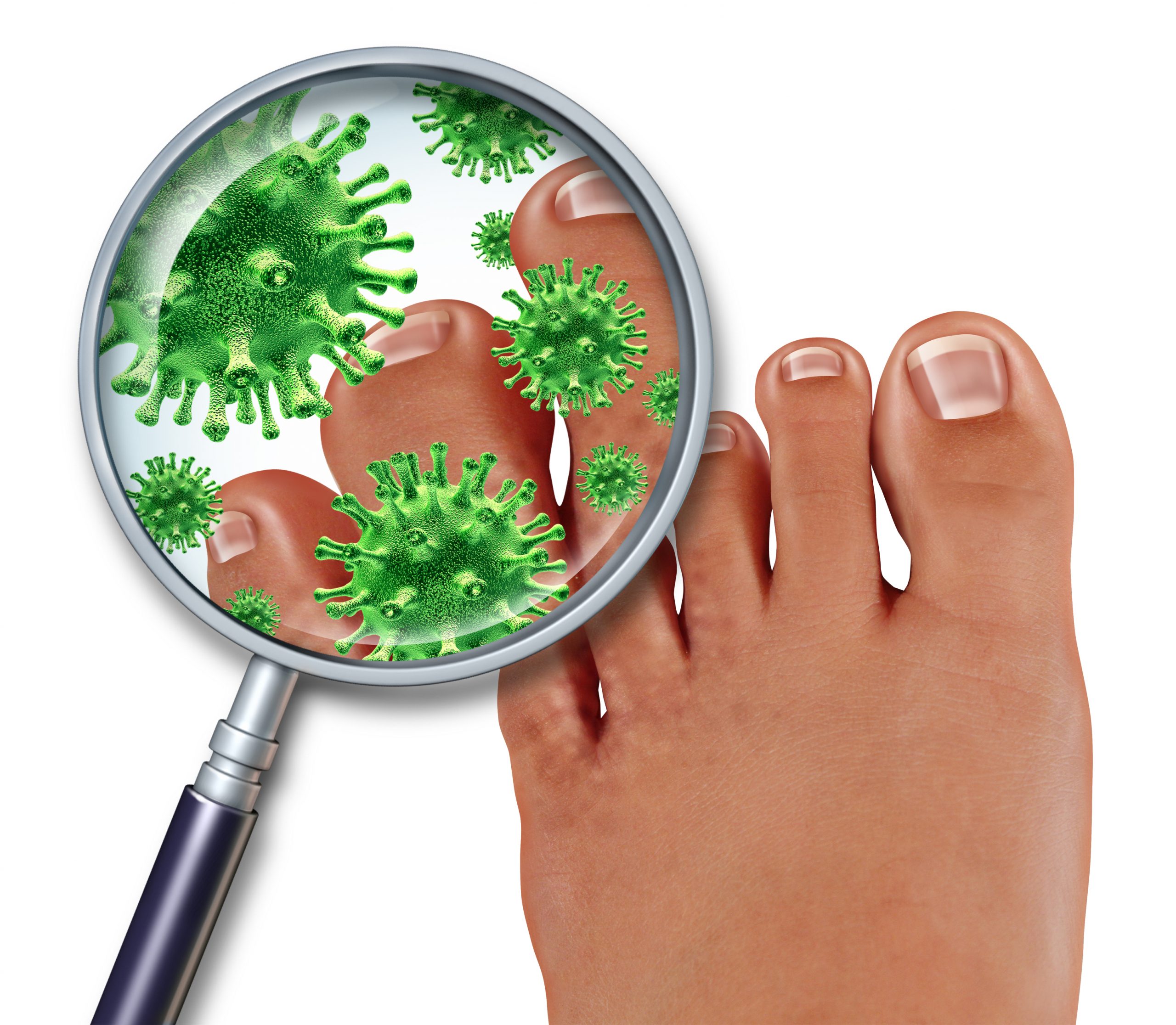
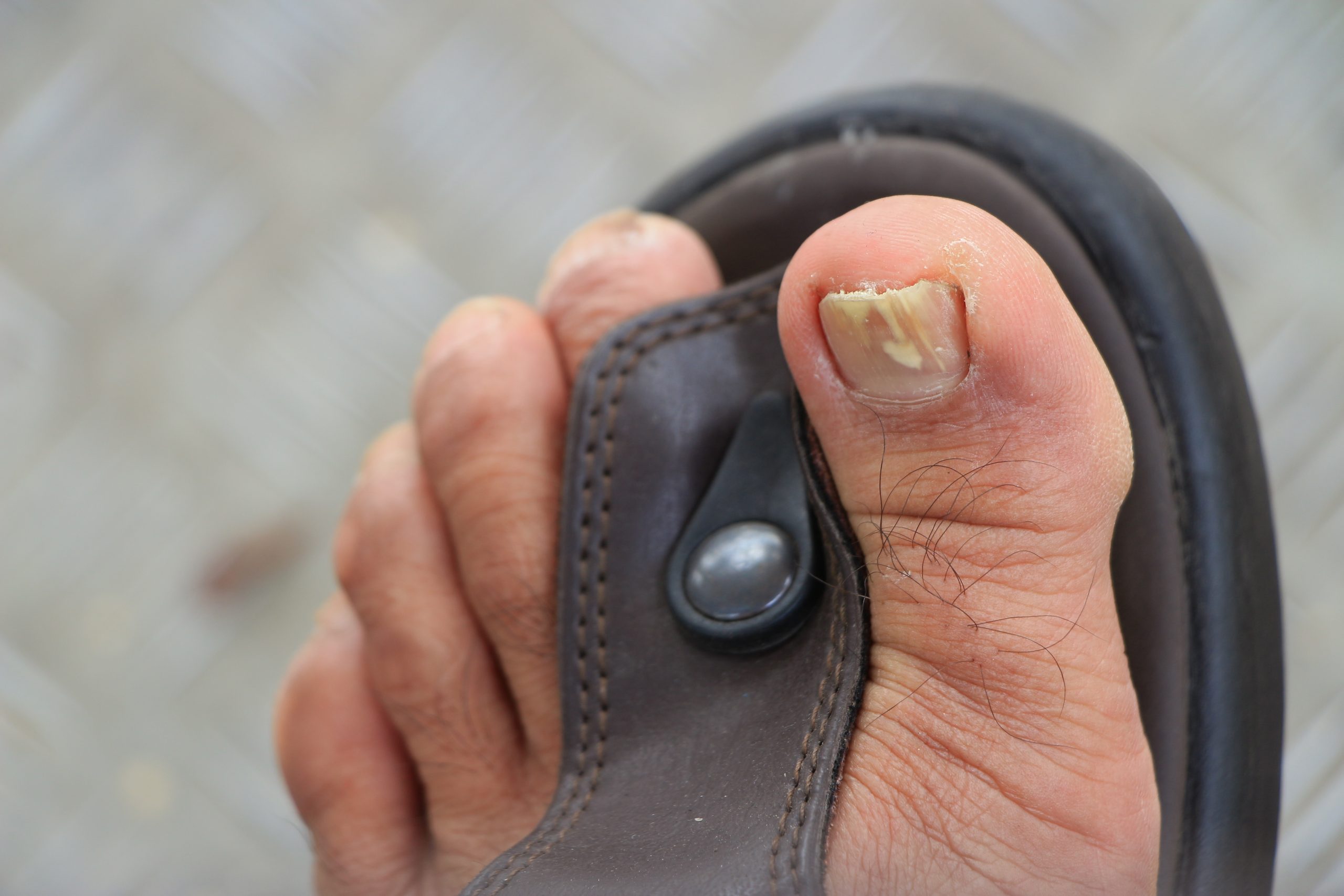
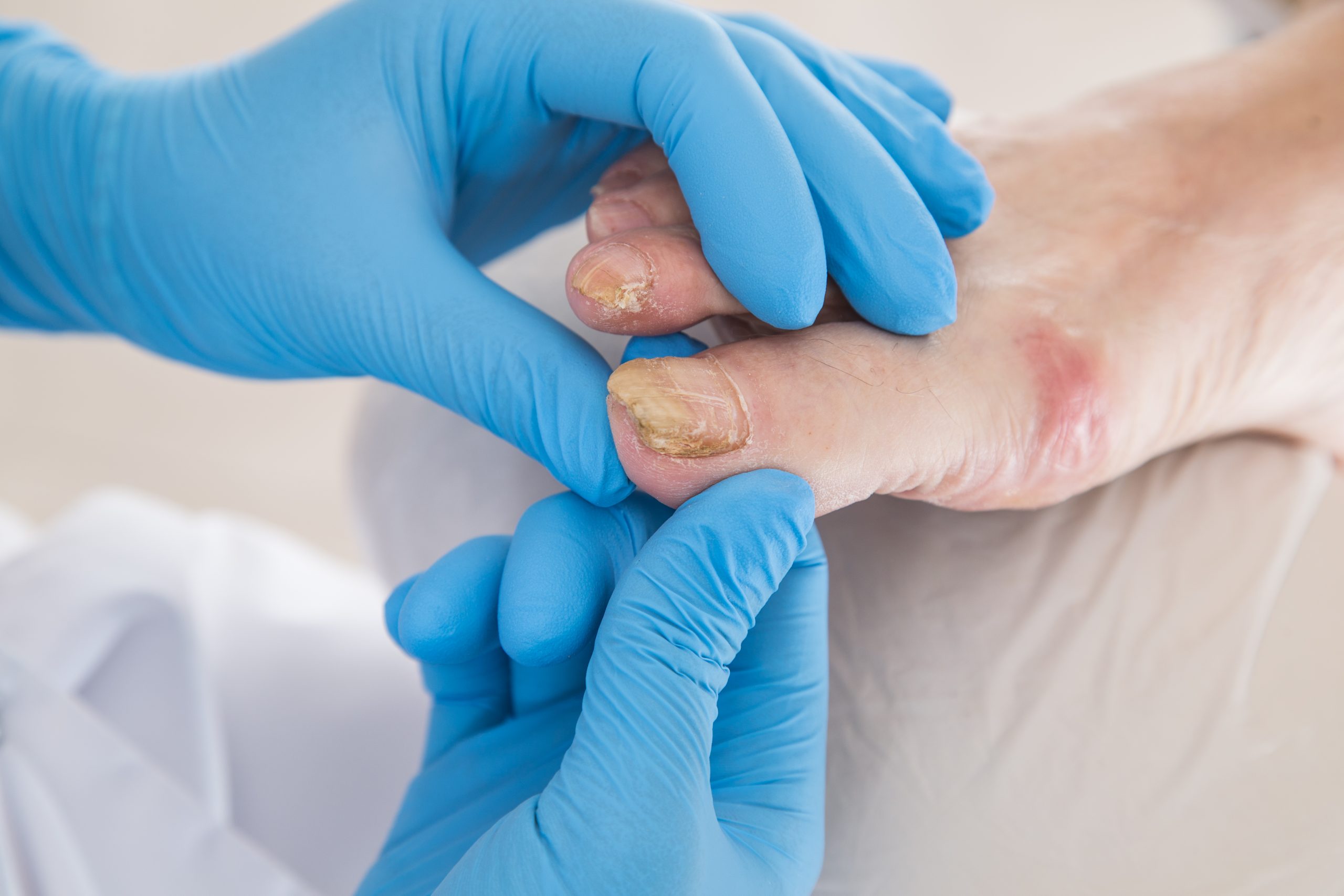
Toenail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when a fungal infection invades the toenail and surrounding area, leading to discoloration, thickening, and brittleness of the nail. While toenail fungus can be unsightly and uncomfortable, understanding the common causes can help prevent its occurrence. In this article, we will explore the primary causes of toenail fungus and how to avoid them.
- Fungal Infection:
The most common cause of toenail fungus is a fungal infection. Fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making your feet susceptible to infection in areas like public swimming pools, communal showers, and locker rooms. Walking barefoot in these environments increases the risk of coming into contact with the fungi responsible for toenail infections.
- Trauma to the Nail:
Nail trauma, such as repetitive microtrauma or a single injury, can create an entry point for fungal infection. For example, stubbing your toe or dropping a heavy object on it can damage the nail bed and allow fungi to invade. Injuries that cause separation of the nail from the nail bed can also make the nail more susceptible to infection.
- Poor Foot Hygiene:
Inadequate foot hygiene is another common cause of toenail fungus. Failing to keep your feet clean and dry, especially after sweating or exposure to moisture, creates an environment where fungi can thrive. It is essential to wash your feet regularly, dry them thoroughly (especially between the toes), and change your socks frequently to prevent fungal growth.
- Tight or Unbreathable Shoes:
Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes can contribute to toenail fungus. Shoes that don’t allow for proper ventilation and moisture control create an environment that is ideal for fungal growth. It is recommended to wear shoes that fit well, provide ample space for your toes, and are made from breathable materials to promote airflow and prevent excessive sweating.
- Weakened Immune System:
Having a weakened immune system can increase the risk of developing toenail fungus. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or undergoing chemotherapy, can compromise the immune system’s ability to fight off infections effectively. Individuals with weakened immune systems should take extra precautions to prevent toenail fungus and seek prompt treatment if an infection occurs.
- Age and Other Health Factors:
As we age, our nails become more brittle and prone to infection. The natural aging process, combined with other health factors like poor circulation, can contribute to the development of toenail fungus. Additionally, conditions that affect blood flow, such as peripheral artery disease, can increase the risk of fungal infections in the toes.
- Sharing Personal Items:
Sharing personal items such as nail clippers, files, or shoes with someone who has toenail fungus can increase your risk of infection. Fungi can survive on these items and be easily transferred to your nails. It is important to avoid sharing personal items and ensure that nail salons and spas follow proper sterilization practices to minimize the risk of infection.
Preventing toenail fungus:
- Practice good foot hygiene by washing your feet regularly and drying them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Wear breathable shoes made from natural materials that provide adequate ventilation.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas, especially where the floor is moist, such as swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers.
- Keep your nails trimmed and avoid cutting them too short, as this can increase the risk of injury and fungal infection.
- Use antifungal sprays or powders in your shoes and on your feet to help prevent fungal growth.
- Avoid sharing personal items like nail clippers,