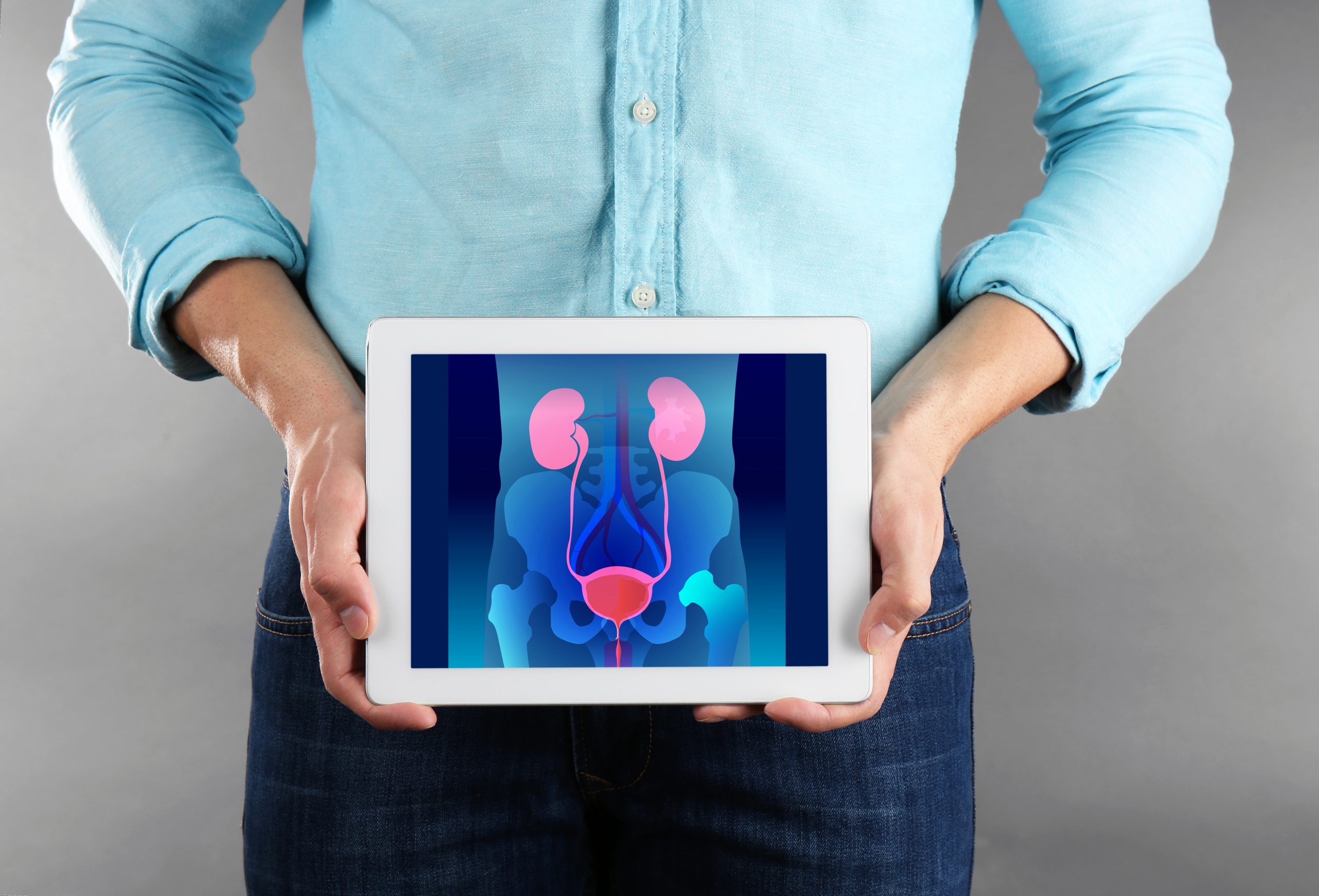
Prostate health is a significant concern for many men as they age, as it can impact various aspects of their well-being, including urinary function. The prostate gland, located below the bladder, plays a crucial role in reproductive health and urinary function. Changes in prostate health can affect urinary flow and lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine stream, or difficulty emptying the bladder. Understanding the connection between prostate health and urinary function is essential for men’s overall health and quality of life. In this article, we will explore the link between prostate health and urinary function and discuss strategies for maintaining a healthy prostate and optimal urinary function.
- Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH): With age, the prostate gland often undergoes benign enlargement, a condition known as BPH. The enlarged prostate can compress the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder, resulting in urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, nocturia (waking up at night to urinate), weak urine stream, or incomplete bladder emptying. Monitoring prostate health and seeking appropriate medical care can help manage BPH symptoms and promote better urinary function.
- Prostatitis: Prostatitis refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be caused by infection or other factors. Inflammation can lead to urinary symptoms such as pain or discomfort during urination, frequent urination, or urgency. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important to address prostatitis and alleviate associated urinary symptoms.
- Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men. While urinary symptoms may not always be present in the early stages, advanced prostate cancer can affect urinary function. Cancerous growth in the prostate can obstruct the urethra and lead to urinary symptoms similar to those of BPH. Regular prostate screenings and early detection are crucial for managing prostate cancer and minimizing its impact on urinary function.
- Urinary Incontinence: In some cases, prostate issues can contribute to urinary incontinence, the unintentional leakage of urine. This can occur due to factors such as prostate surgery or damage to the nerves and muscles responsible for urinary control. Pelvic floor exercises, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions can help manage urinary incontinence and restore bladder control.
- Interference with Urinary Flow: Prostate conditions, such as BPH or prostate cancer, can obstruct the normal flow of urine. This can lead to urinary retention, where the bladder does not completely empty during urination. Incomplete bladder emptying can increase the risk of urinary tract infections and other urinary complications. Seeking medical attention and adopting strategies to promote healthy urinary flow are important for preventing further complications.
- Impact on Sexual Function: Prostate health can also impact sexual function and urinary control during sexual activity. Prostate conditions or treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, can affect erectile function and ejaculatory control. Open communication with healthcare providers and exploring appropriate treatment options can help manage any sexual or urinary changes resulting from prostate-related issues.
- Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle factors can influence both prostate health and urinary function. Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can support overall prostate health and urinary function. Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol intake can also promote a healthy urinary system.
- Regular Prostate Screenings: Regular prostate screenings, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests and digital rectal examinations, are crucial for monitoring prostate health and detecting any abnormalities early. Age, family history, and individual risk factors play a role in determining the appropriate frequency and timing of prostate screenings. Consultation with a healthcare provider can help