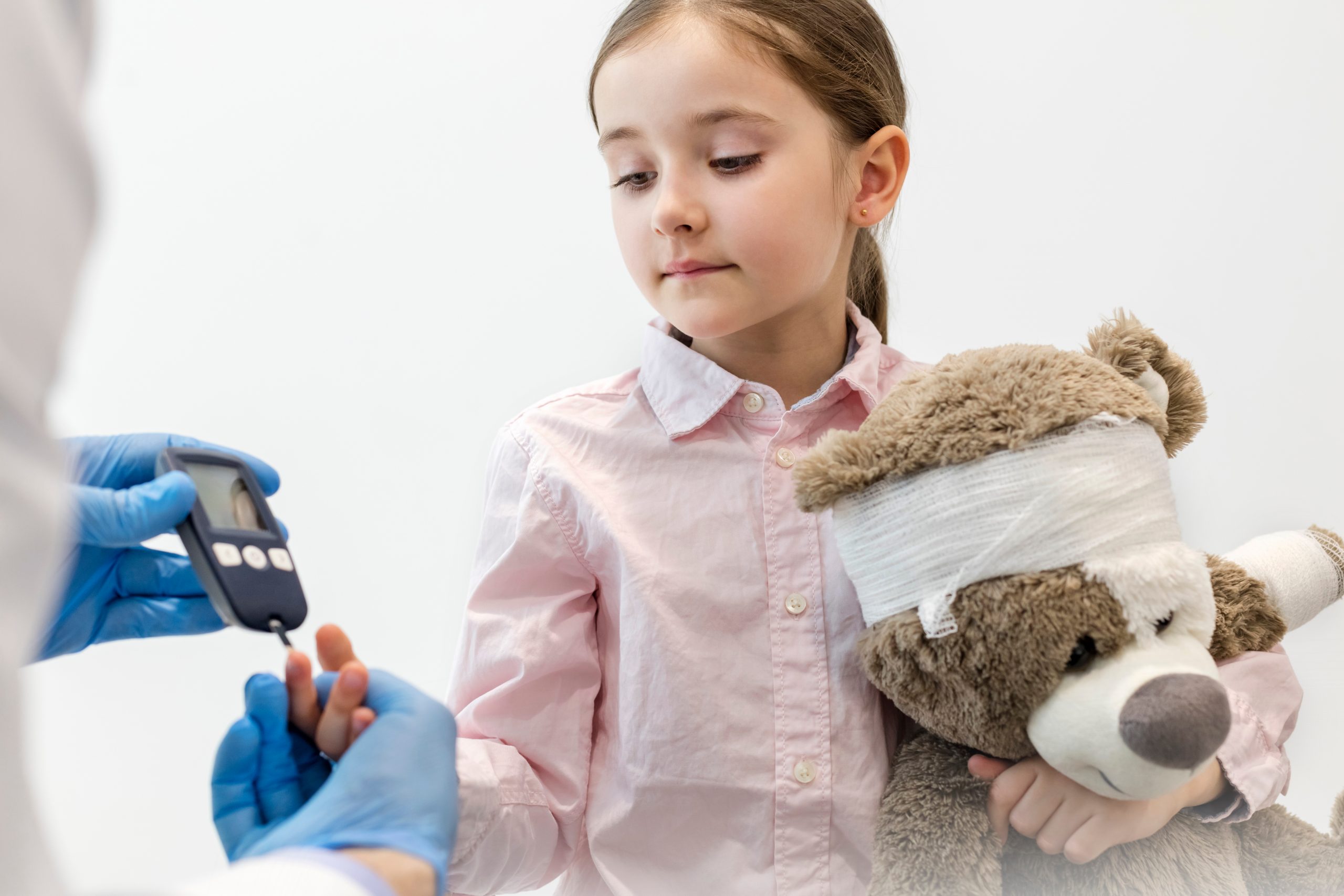
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While diabetes is commonly associated with adults, it can also affect children. In fact, according to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 193,000 Americans under the age of 20 have diabetes. In this article, we’ll explore some of the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for diabetes in children.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes in Children
The signs and symptoms of diabetes in children can vary depending on the type of diabetes they have. The two main types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels in the body. Without insulin, blood sugar levels can rise to dangerous levels. Some signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Unintended weight loss
- Irritability or mood changes
- Bedwetting in children who were previously dry at night
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Some signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Hunger, even after eating
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts or sores
- Darkened areas of skin
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
- Treatment Options for Diabetes in Children
The treatment options for diabetes in children can vary depending on the type of diabetes they have. For type 1 diabetes, treatment typically involves insulin therapy. This can include injections or the use of an insulin pump to deliver insulin into the body. Additionally, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help manage symptoms.
For type 2 diabetes, treatment may involve making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. In more severe cases, insulin therapy may be necessary.
Managing Diabetes in Children
Managing diabetes in children can be a challenging and complex process. It’s important for parents and caregivers to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a management plan that works best for their child. This can include monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, adjusting medication dosages as needed, and making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.
Additionally, it’s important for parents and caregivers to educate themselves and their child about diabetes and how to manage it. This can include teaching children how to recognize the signs and symptoms of high or low blood sugar levels and how to manage them.
In conclusion, diabetes is a chronic condition that can affect children as well as adults. It’s important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of diabetes in children and to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a management plan that works best for their child. With proper management and treatment, children with diabetes can lead happy and healthy lives.