As we age, changes occur throughout our bodies, and our hair is no exception. Hair growth and quality can be affected by various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and overall health. Understanding the impact of aging on hair growth can help individuals make informed decisions and take proactive steps to maintain healthy hair. In this article, we will explore the effects of aging on hair growth and provide tips for promoting hair health as we grow older.
- Reduced Hair Thickness: One of the most noticeable changes in hair with aging is a decrease in hair thickness. Hair strands become finer and may appear less dense. This thinning effect is more common in both men and women as they age. It is influenced by factors such as hormonal changes, reduced blood flow to the hair follicles, and decreased production of natural oils that nourish the scalp and hair.
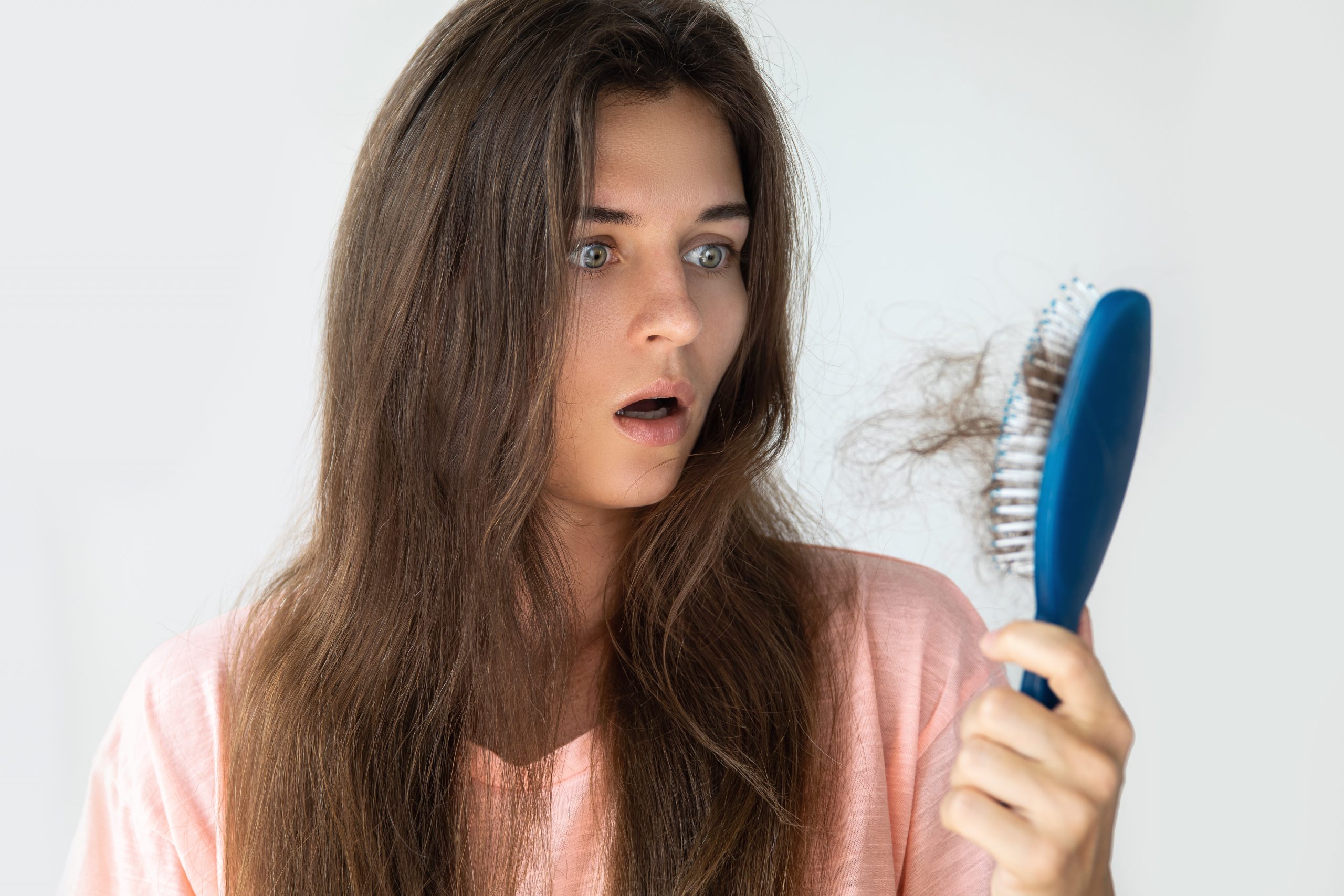
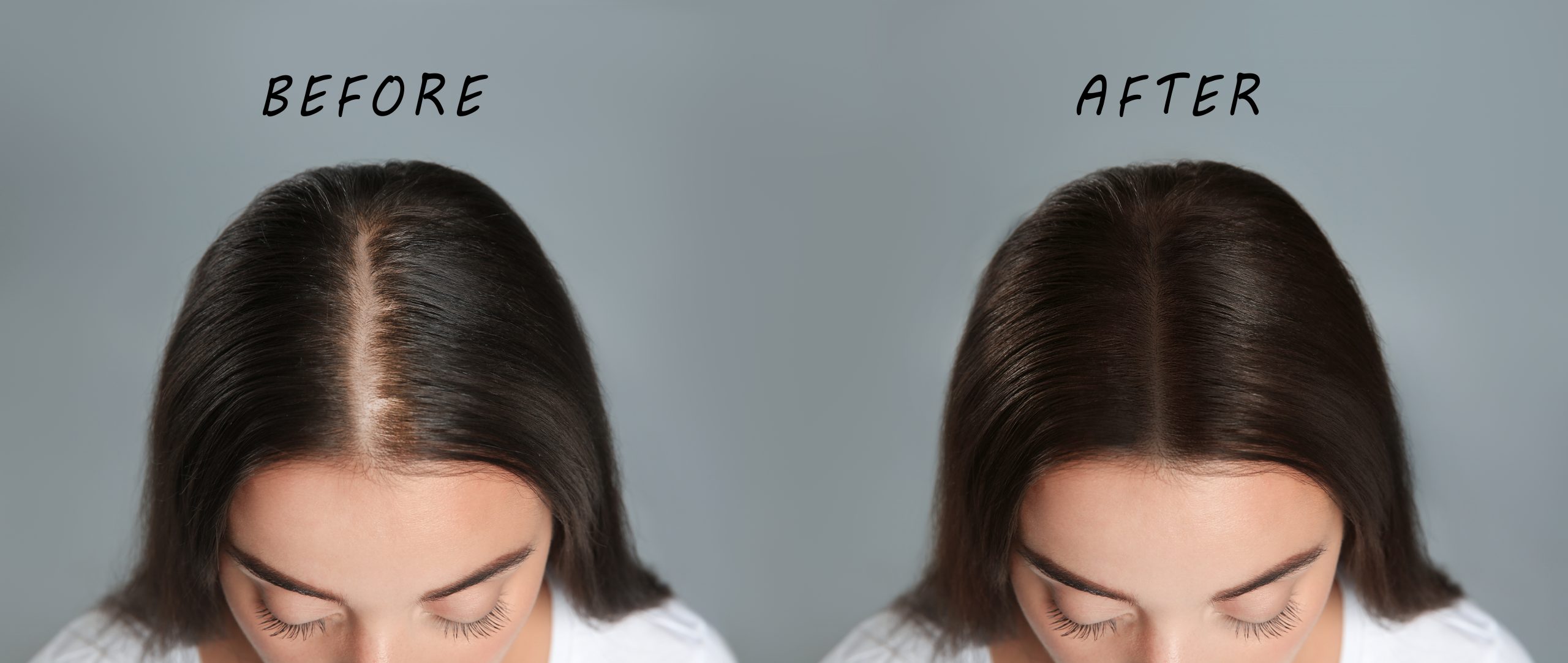
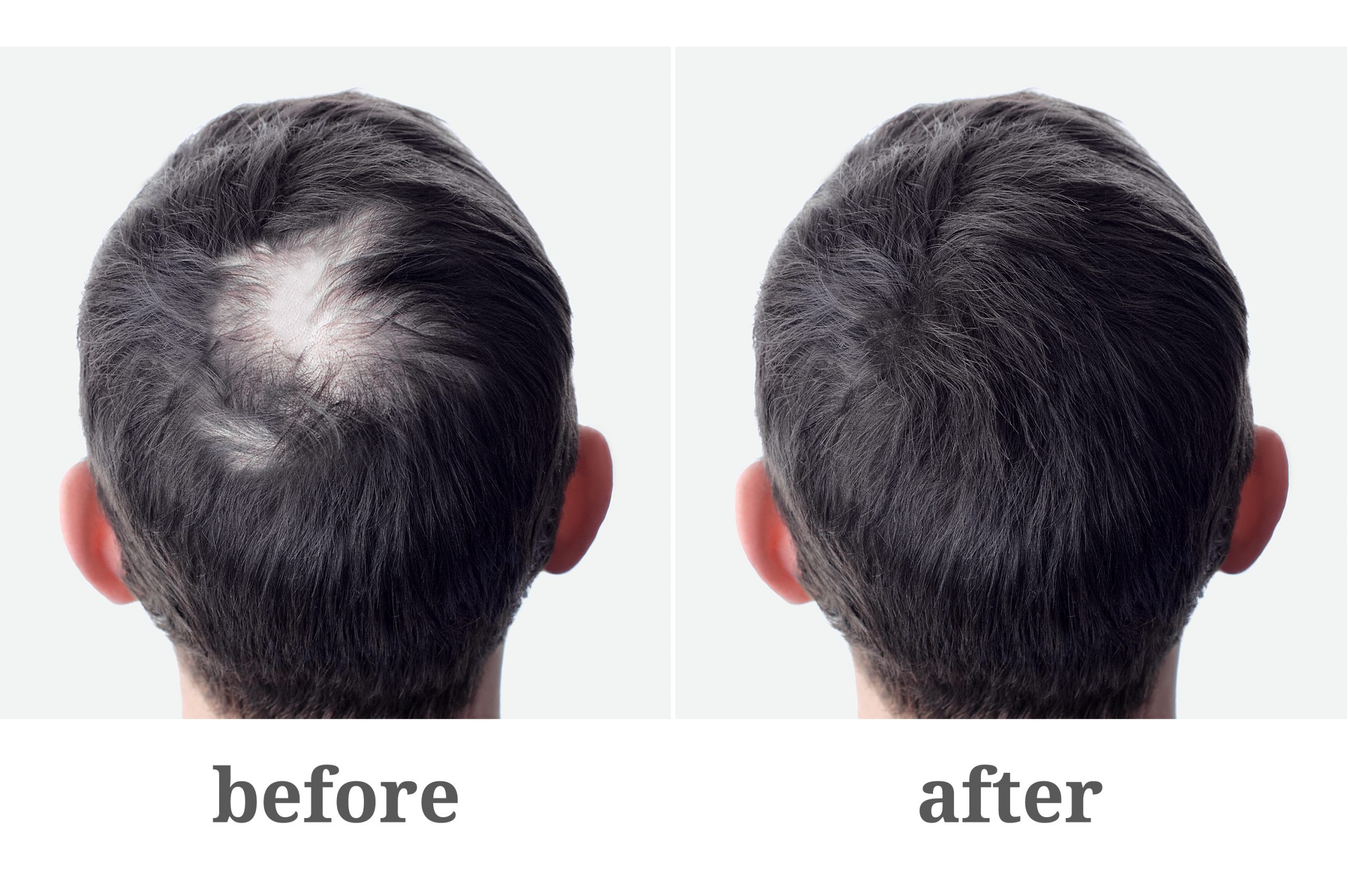
- Increased Hair Loss: Age-related hair loss, known as androgenetic alopecia, is more common in men but can also affect women. It is characterized by a gradual thinning of the hair, especially at the crown or temples. Hormonal changes, specifically the influence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a role in this type of hair loss. Additionally, factors like genetics, stress, and underlying health conditions can contribute to increased hair shedding and reduced hair volume.
- Slower Hair Growth: Hair growth rate tends to slow down with age. The hair growth cycle becomes longer, resulting in less frequent hair turnover. This means that it takes longer for new hair to grow and replace shedding hair. While individual hair growth rates vary, it is common for hair to grow at a slower pace as we age.
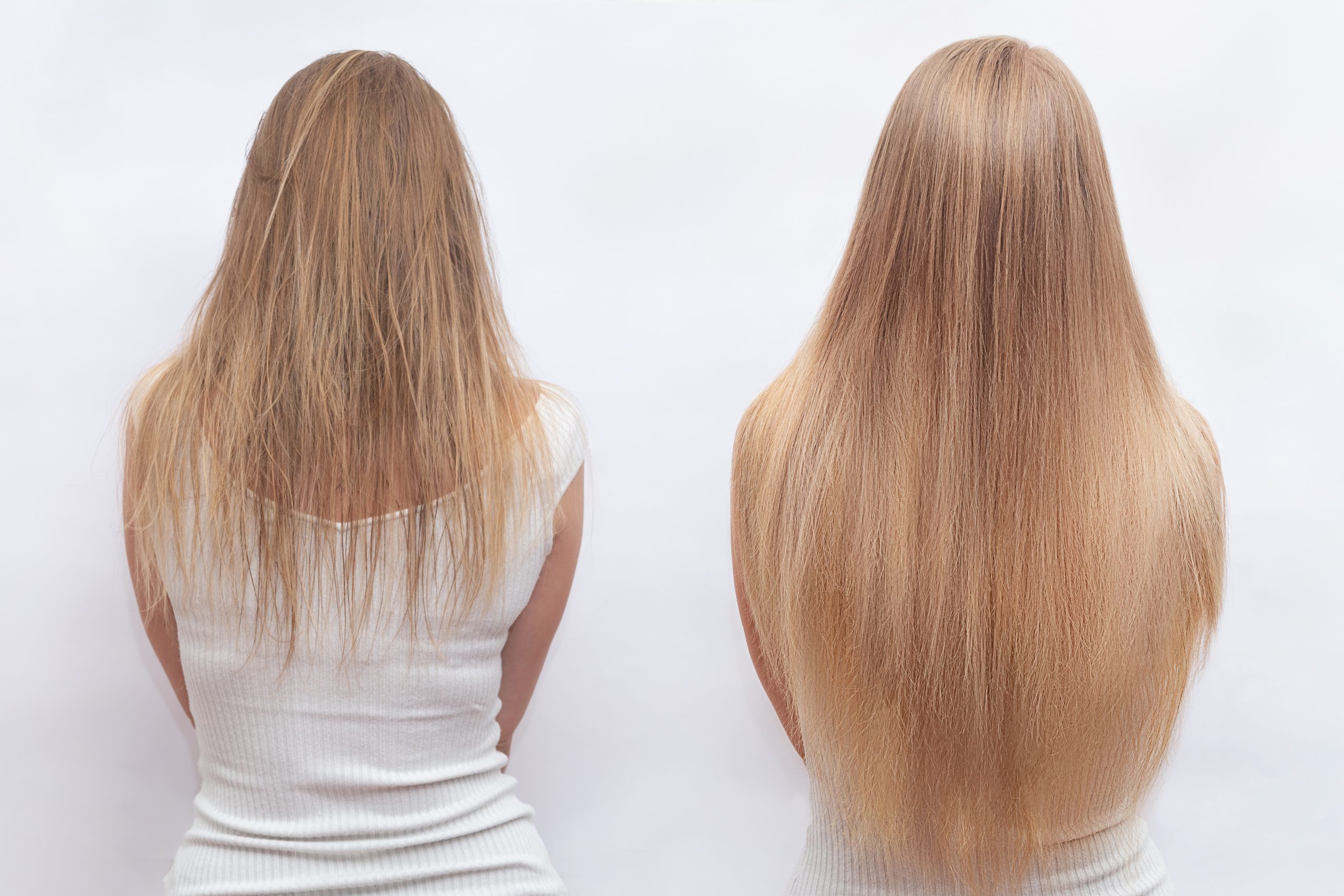
- Changes in Hair Texture: Aging can also affect hair texture. Hair may become drier, more brittle, and more prone to breakage. This change is partly due to reduced oil production from the scalp and decreased moisture retention in the hair shaft. Additionally, hormonal changes and exposure to environmental factors over time can contribute to changes in hair texture and quality.
- Gray Hair: Graying hair is a natural part of the aging process. As we age, the pigment-producing cells in the hair follicles, called melanocytes, gradually produce less melanin. Melanin is responsible for hair color, and as its production decreases, hair turns gray or white. The timing and extent of graying hair vary among individuals and are influenced by genetics.
Tips for Promoting Healthy Hair as You Age:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet plays a crucial role in hair health. Ensure you consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients for hair growth. Include foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and B-complex vitamins, as well as minerals like zinc, iron, and biotin.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water to keep your body and hair hydrated. Proper hydration supports overall hair health and can help minimize dryness and brittleness.
- Protect Hair from Damage: Be mindful of how you style and treat your hair. Avoid excessive heat styling, harsh chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that can cause tension and damage to the hair shaft. Use heat protectant sprays and gentle hair care products.
- Gentle Hair Care Routine: Use mild shampoos and conditioners that are suitable for your hair type. Avoid overwashing, as it can strip the hair of natural oils. Be gentle when towel-drying and brushing your hair to minimize breakage.
- Scalp Care: Maintain a healthy scalp by keeping it clean and well-nourished. Regularly cleanse your scalp to remove excess oil and product buildup. Massage your